
TOP STORY
CXO Monthly Roundup, July 2025: Ransomware Report, China-Nexus APT Analysis, SharePoint Security with Zero Trust, and More
Aug 14, 2025
Highlights from the Zscaler ThreatLabz team's July 2025 research.
The CXO Monthly Roundup provides the latest ThreatLabz research, alongside insights on other cyber-related subjects that matter to technology executives. This July edition highlights three major developments: the release of the Zscaler ThreatLabz 2025 Ransomware Report, a detailed analysis of nation-state attacks targeting the Tibetan community, and how Zscaler Deception proactively intercepted exploitation attempts targeting SharePoint servers, providing organizations with critical early warnings days ahead of public advisories. In addition, I cover noteworthy threat updates regarding ransomware and malware developments.
Zscaler ThreatLabz 2025 Ransomware Report
The Zscaler ThreatLabz 2025 Ransomware Report highlights an increase in ransomware activity blocked by the Zscaler cloud and a rise in public extortion cases. ThreatLabz researchers conducted their analysis from April 2024 to April 2025, drawing insights from public data leak sites, Zscaler's proprietary threat intelligence, ransomware samples, attack data, and telemetry from the Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange.
Here are five important takeaways from this year’s report:
- Ransomware attacks surged 145.9% year-over-year, reaching record numbers blocked by Zscaler.
- Public extortion cases rose 70.1%, with more organizations appearing on leak sites.
- Data exfiltration volumes increased 92.7%; 238.5 TB was stolen by 10 major ransomware families, fueling extortion.
- Manufacturing, Tech, and Healthcare remain prime targets, while Oil & Gas (+935%) and Government (+235%) saw significant increases, as shown in the figure below.
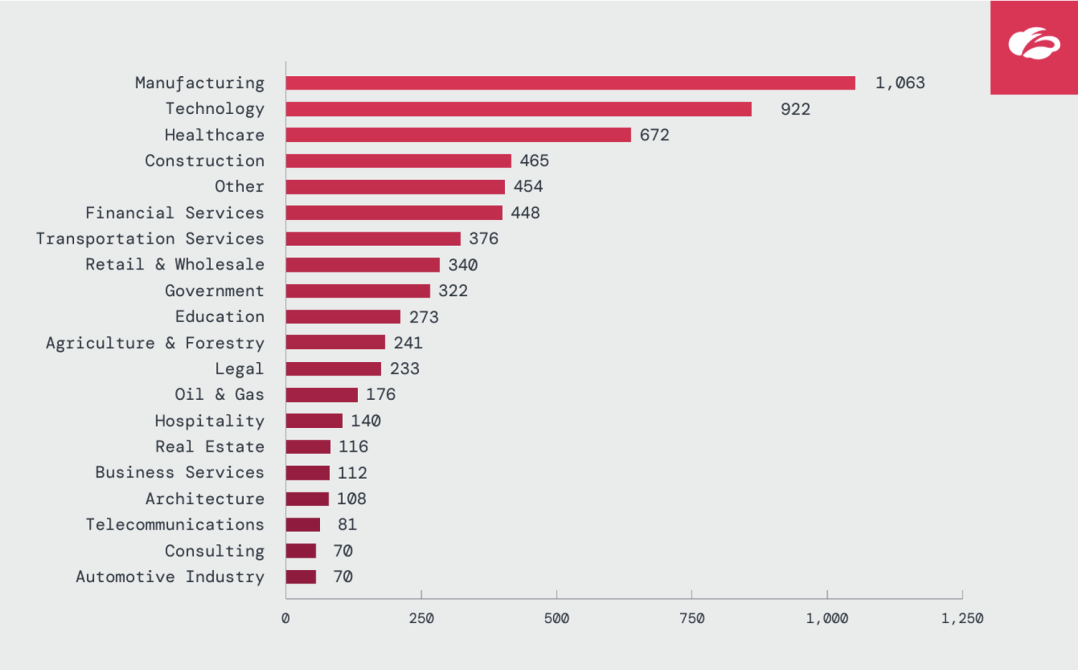
Figure 1: Graph showcasing the industry sectors most targeted by ransomware groups.
- Ransomware groups are rapidly evolving, with 34 new groups emerging, including rebrands and offshoots, filling voids left by disruptions.
Combating ransomware attacks
The Zscaler ThreatLabz 2025 Ransomware Report offers crucial guidance for defending against ransomware. Key takeaways include:
- Neutralizing AI threats with AI-driven strategies: Learn about Zscaler’s AI-powered cyberthreat protection capabilities designed to counter AI-driven threats.
- Advantages of Zero Trust architecture: Learn how the Zero Trust Exchange effectively stops ransomware at every stage of the attack cycle.
- Ransomware prevention checklist: Access the latest best practices to reduce ransomware risk and safeguard your organization from current and future threats.
Zscaler ThreatLabz 2025 Ransomware Report
Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange Coverage - Advanced Cloud Sandbox, Advanced Threat Protection, Advanced Cloud Firewall, SSL Inspection, Deception, Identity Protection.
Operation GhostChat and PhantomPrayers: Unveiling China-Nexus APT Operations
ThreatLabz has published a technical analysis on two cyberattack campaigns targeting the Tibetan community. The attacks, named Operation GhostChat and Operation PhantomPrayers, capitalized on increased online activity around the Dalai Lama's 90th birthday to distribute malware in multi-stage attacks. Our analysis outlines how the attackers compromised a legitimate website, redirecting users via a malicious link and ultimately installing either the Ghost RAT or PhantomNet (SManager) backdoor onto victim systems. Both operations were attributed to China-nexus APT groups based on the victimology, malware (Ghost RAT and PhantomNet) usage, and techniques, as shown in the diamond model below.
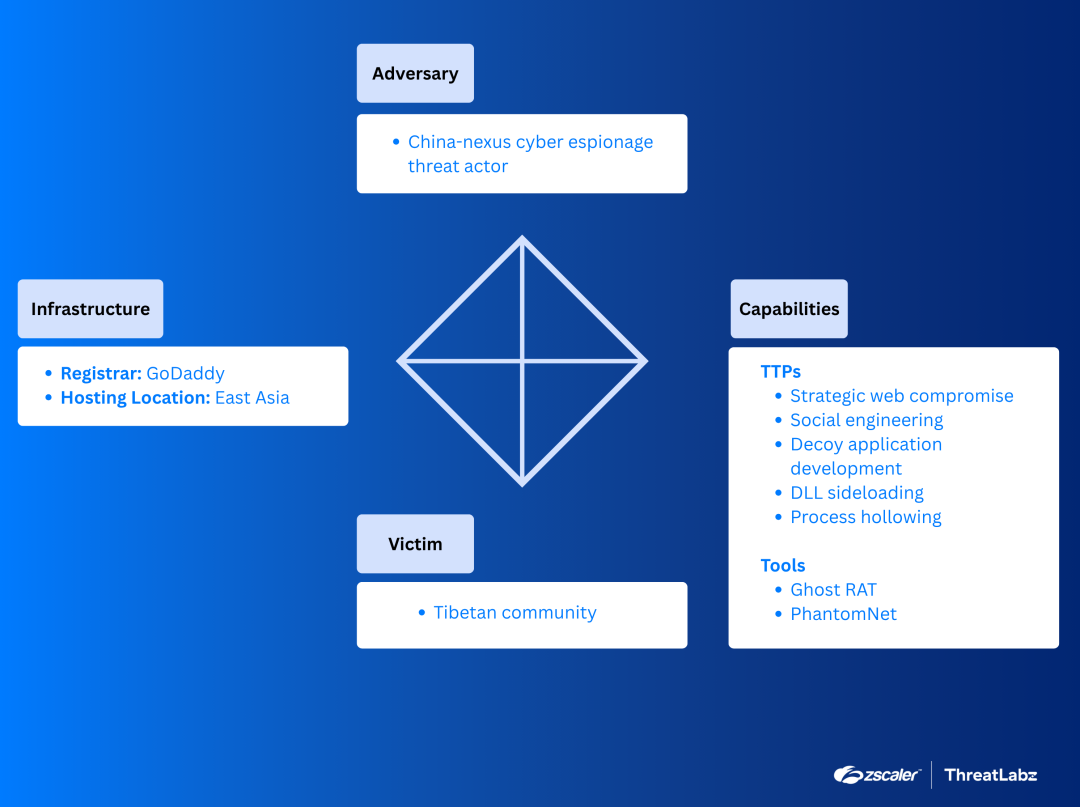
Figure 2: Diamond model highlighting key attributes of this campaign that delivers Ghost RAT and PhantomNet and targets the Tibetan community.
Operation GhostChat
Operation GhostChat involved threat actors redirecting users to a malicious website (thedalailama90.niccenter[.]net) that hosted a backdoored version of Element, an encrypted chat application. This version of Element used DLL sideloading to execute Ghost RAT malware. Ghost RAT facilitates file manipulation, video and audio capture, keylogging, and system shutdowns. Ghost RAT evades detection through advanced techniques such as code injection, dynamic API resolution, and user-mode API overwriting. Additionally, JavaScript-based IP collection was used for further surveillance and exploitation. The figure below shows the attack sequence associated with Operation GhostChat that ultimately delivers Ghost RAT.
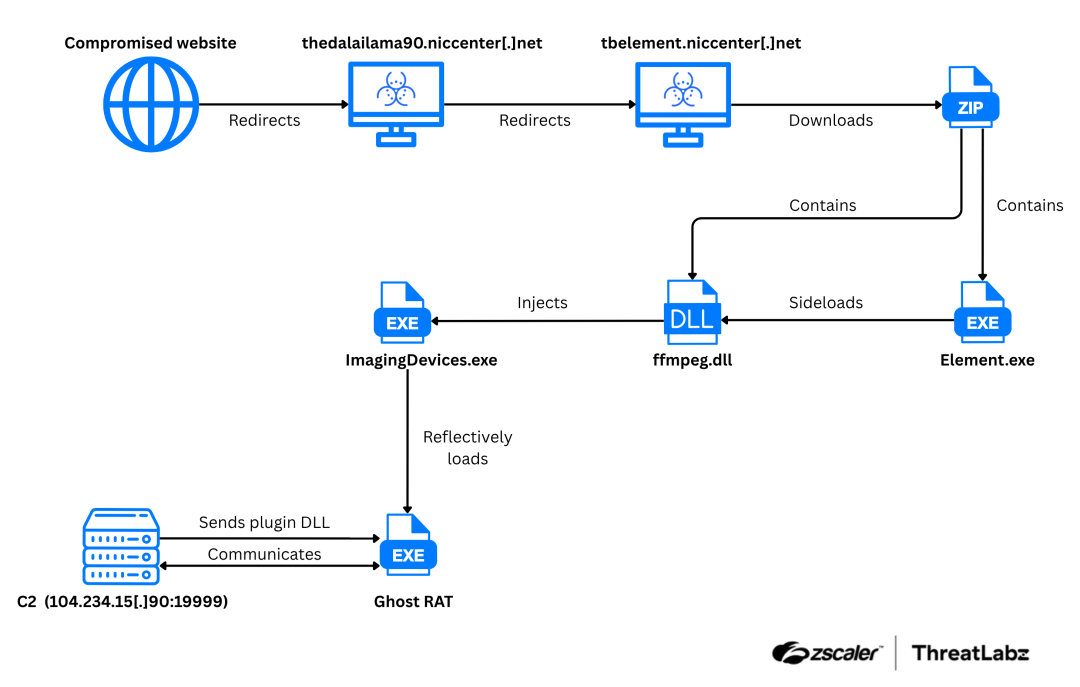
Figure 3: Shows the attack sequence associated with Operation GhostChat that ultimately delivers Ghost RAT.
Operation PhantomPrayers
Operation PhantomPrayers deployed malware disguised as a "prayer check-in" application, distributed via the malicious domain hhthedalailama90.niccenter[.]net. The malware, a PyInstaller-based executable, presented a deceptive graphical interface to collect personal information from the victim. Once installed, the malware achieved persistence through shortcut files and injected malicious code using DLL sideloading with VLC.exe. The attack's core was the multi-stage deployment of the PhantomNet backdoor. PhantomNet collects system information, manipulates the Windows registry, enables remote shell access, and performs various stealthy administrative tasks. To avoid detection, Operation PhantomPrayers employed advanced encryption (RC4 and AES) for shellcode, reflective code loading for memory-based execution, and modular plugin DLLs for dynamic functionality. The figure below shows the attack sequence associated with Operation PhantomPrayers that ultimately delivers PhantomNet.
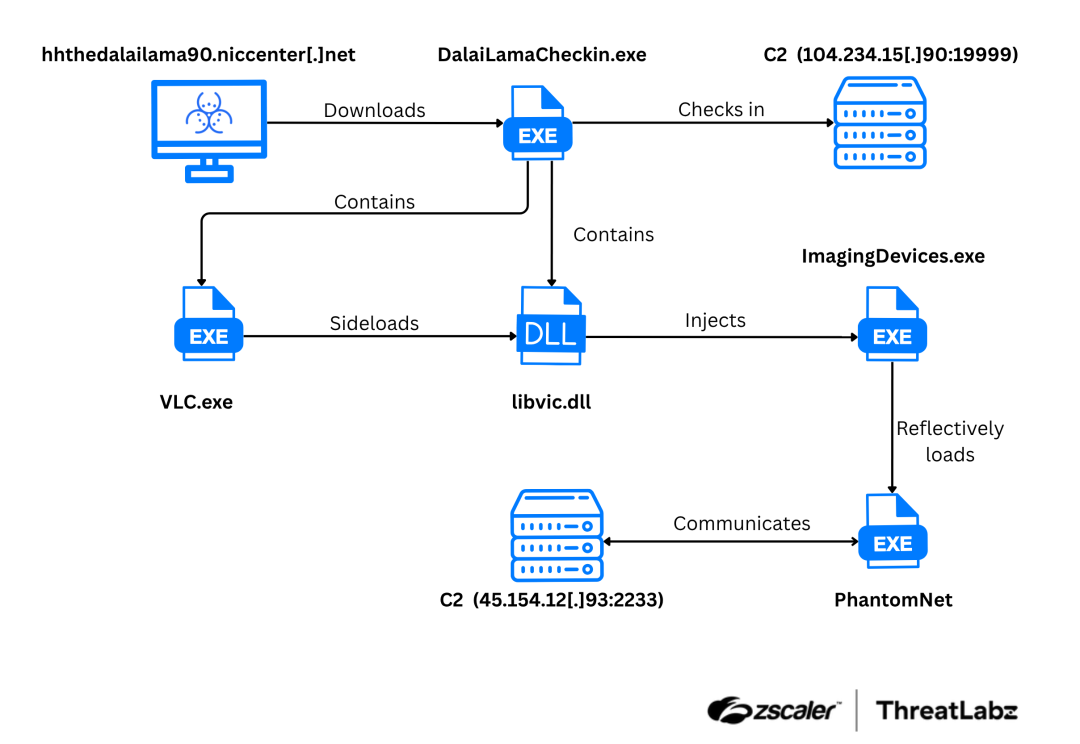
Figure 4: Shows the attack sequence associated with Operation PhantomPrayers that ultimately delivers PhantomNet.
Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange Coverage – Zscaler Internet Access (Advanced Cloud Sandbox, Advanced Threat Protection, SSL Inspection), Zscaler Private Access, Deception
Protecting On-Premises SharePoint from ToolShell Exploits: Zscaler’s Zero Trust Approach
On July 19, 2025, Microsoft published an advisory on CVE-2025-53770, a critical zero-day vulnerability known as ToolShell, which targets SharePoint’s insecure server-side data handling to enable unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE). ToolShell exploits cryptographic secrets, such as the ValidationKey, to craft malicious payloads, bypass authentication, and gain control of vulnerable servers. The figure below shows the attack flow CVE-2025-53770 follows to achieve RCE on a SharePoint server.
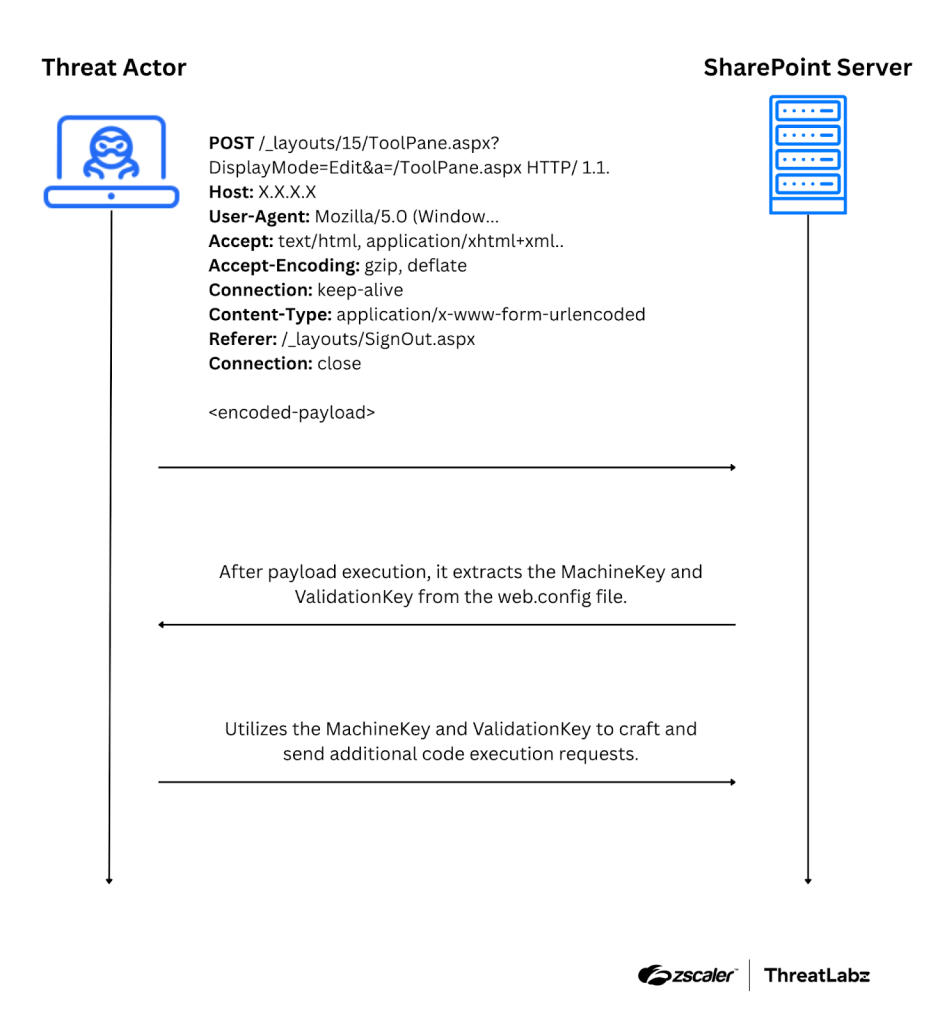
Figure 5: Diagram shows how the CVE-2025-53770 attach chain works.
Detecting and preventing exploits
Early detection and rapid response are critical in stopping cyberattacks before they can cause widespread damage. I recently wrote about how Zscaler Deception intercepted malicious activity targeting SharePoint servers, providing decisive early warning to organizations days before public advisories were issued.
On July 17th, Zscaler Deception began detecting exploit attempts against perimeter-facing SharePoint environments—four days before CISA’s advisory went public. By deploying decoys designed to mimic real SharePoint environments, ThreatLabz successfully identified exploitation attempts, collected threat intelligence, and preemptively blocked attackers from advancing. These early threat signals allowed affected organizations to mitigate risks before lateral movement could occur.
Zscaler's layered approach integrates Zscaler Deception for proactive threat detection with Zscaler Private Access (ZPA) to contain and neutralize threats. ZPA isolates compromised accounts, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive systems like Teams or OneDrive. The Zero Trust Exchange further strengthens defenses by moving vulnerable servers behind secure perimeters, reducing external attack exposure.
Recommendations for mitigation
Organizations can reduce risks from ToolShell using a proactive security strategy:
- Patch immediately: Implement Microsoft's emergency fixes for affected SharePoint server versions immediately. However, note that this is not a complete solution.
- Adopt a Zero Trust architecture: To minimize exposure and reduce the risk of compromise, move vulnerable servers, including legacy systems, behind Zscaler’s Zero Trust Exchange.
- Implement ZPA: Isolate compromised accounts or insider threats to prevent lateral movement across network environments.
- Deploy Zscaler Deception: Use decoys to detect exploitation attempts and gather critical threat intelligence and benefit from the collective intelligence of Zscaler’s community. These decoys provide visibility into real-time exploitation.
- Enhance monitoring: Continuously audit logs, monitor endpoints, and look for malicious indicators such as deserialization attempts and unusual file system activity.
Preventative action is crucial
ToolShell highlights legacy infrastructure vulnerabilities, stressing the need for proactive cybersecurity. Zscaler's Deception, ZPA, and Zero Trust Exchange offer potent defenses, intercepting threats before they can cause damage.
Prevalent Threat Updates
The following ransomware and malware developments emphasize the dynamic nature of cyber threats and highlight the importance of staying vigilant to adapt defense strategies effectively.
- Rhadamanthys variant: Zscaler ThreatLabz has uncovered a new version of the Rhadamanthys malware, showing changes in its internal structure.
- BlackSuit ransomware: The BlackSuit ransomware group's activities appear to have been disrupted as part of Operation Checkmate, with their negotiation portal and data leak website now displaying a seizure notice.
- Bumblebee and DonutLoader distribution: ThreatLabz observed the Bumblebee malware delivering DonutLoader, which is embedded with the StealC V2 information stealer.
About ThreatLabz
ThreatLabz is the embedded research team at Zscaler. This global team includes security experts, researchers, and network engineers responsible for analyzing and eliminating threats across the Zscaler security cloud and investigating the global threat landscape. The team shares its research and cloud data with the industry at large to help promote a safer internet.
The Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange
Zscaler manages the world’s largest security cloud. Each day, Zscaler blocks over 150 million threats to its more than 9,000 customers, securing over 500 billion web transactions daily. The Zscaler ThreatLabz security research team uses state-of-the-art AI/ML and machine-learning technology to analyze Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange traffic and share its findings.
Recommended
